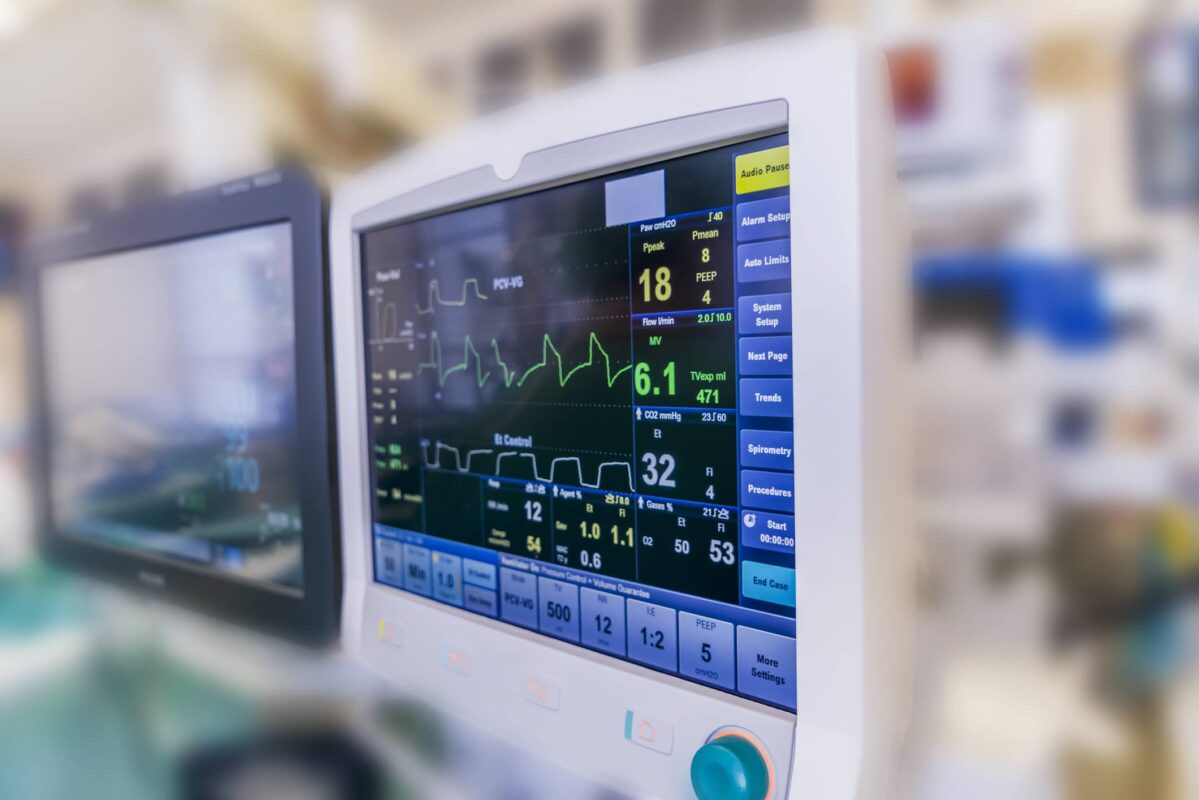
Biomedical signal processing involves acquiring, pre-processing and modeling physiological signals to identify patterns and signals.
Sources can include neural activity, cardiac rhythm, muscle movement, and other physiological activities, for example via an electrocardiogram (ECG), an electroencephalogram (EEG), and electromyography (EMG) used for diagnosis and as indicators of overall health.
KX facilitates a workflow including signal acquisition, visualization and annotation, with pre-processing and feature extraction driving into classification and predictive models and/or used directly for diagnosis.
In either case, there is easy interoperability with production Python code or research-oriented Jupyter Notebooks for training and calibrating predictive models that, once trained, validated, and exported as inferred models, can perform live diagnosis in real-time.